New Research Reveals the Changing Landscape of Vulnerability Exploitation
Exciting new statistics from cybersecurity firm Mandiant shed light on the evolving tactics of attackers exploiting vulnerabilities. The analysis, based on 138 different vulnerabilities disclosed in 2023, uncovers some alarming trends in the world of cyber threats.
The report, recently published on Google Cloud’s blog, points to a concerning rise in attacks targeting vendors. Attackers are now able to exploit both zero-day and N-day vulnerabilities at an unprecedented speed, reducing the average time to exploit to just 5 days in 2023.
The Significant Decline in Time-to-Exploit
Time-to-exploit (TTE) measures the average duration between the release of a patch and the successful exploitation of a vulnerability. The data revealed by Mandiant shows a noticeable decrease in TTE over the years:
- 2018-2019: 63 days
- 2020-2021: 44 days
- 2021-2022: 32 days
- 2023: 5 days
This rapid reduction in TTE indicates a growing efficiency among attackers in exploiting vulnerabilities before patches can be effectively deployed.
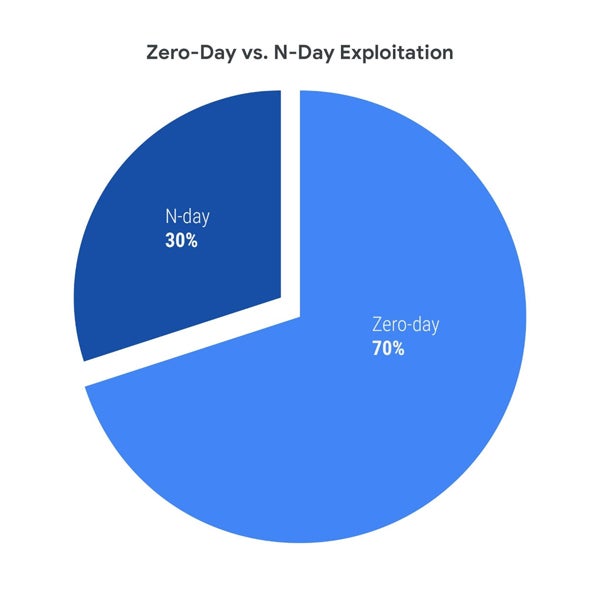
Zero-day vs N-day Exploits
As attackers capitalize on shrinking TTE windows, they are increasingly targeting both zero-day (unpatched) and N-day (known but unpatched) vulnerabilities. In 2023, an upsurge in zero-day exploit usage was observed, leading to a shift in the ratio of N-day to zero-day exploits to 30:70, compared to 38:62 in the previous period.
Mandiant’s researchers, Casey Charrier and Robert Weiner, suggest that this change reflects a higher reliance on zero-day exploits by threat actors, signaling a concerning trend in the cybersecurity landscape.
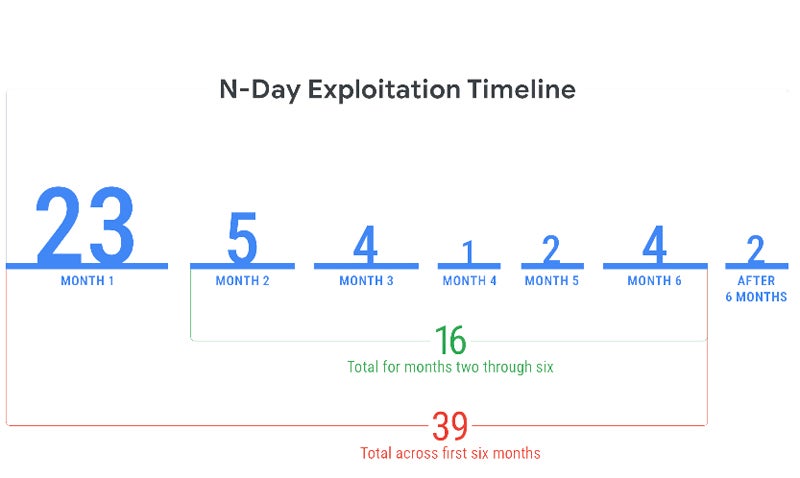
Exploitation Patterns of N-day Vulnerabilities
Mandiant’s research indicates that N-day vulnerabilities are often exploited in the initial month following the release of patches. Within the first month, 23 N-day vulnerabilities were targeted, with a significant percentage exploited within a week of patch availability.
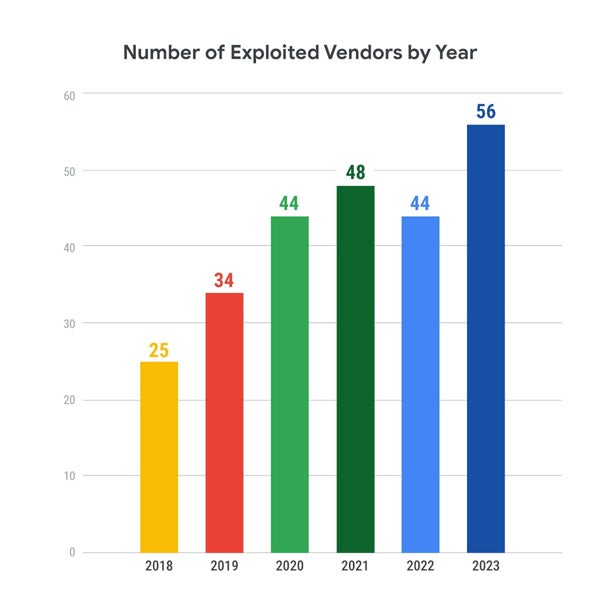
Increasing Targeting of Vendors
Attackers are expanding their scope to target more vendors, with the number rising from 25 in 2018 to 56 in 2023. This growing diversity of targets presents a greater challenge for defenders in securing their systems.
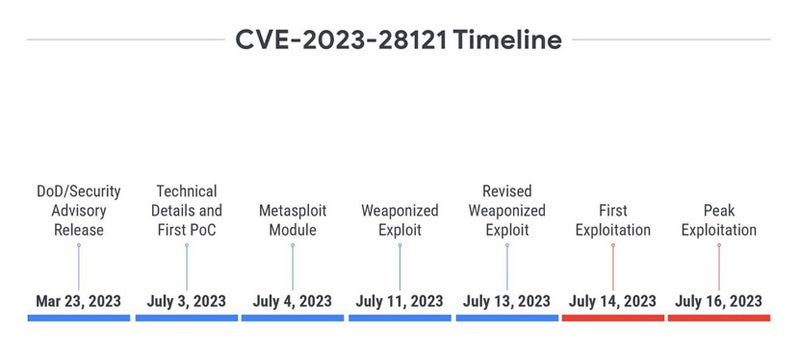
Case Studies Highlighting Severity of Exploitations
Mandiant’s analysis delves into specific cases, such as the CVE-2023-28121 vulnerability in the WooCommerce Payments plugin for WordPress. The rapid exploitation of this vulnerability underscored the urgency of patch deployment and highlighted the challenges faced by defenders in a rapidly evolving threat landscape.
The case of CVE-2023-27997, known as XORtigate, reflects a different timeline and level of exploitation complexity, shedding light on the varying degrees of risk associated with different vulnerabilities.

Challenges in Deploying Patches
While patching is crucial to address vulnerabilities, the process is not without its challenges. Fred Raynal of Quarkslab emphasizes the complexities involved in patch deployment, highlighting the intricate ecosystem of software updates and the diverse considerations that organizations must navigate.
As the threat landscape continues to evolve, the imperative for timely patch deployment and proactive cybersecurity measures grows stronger. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and stay protected against emerging cyber threats.


