The Changing Landscape of Cybercrime: Insights from HP Wolf Security
In the ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, cybercriminals are constantly adapting and refining their techniques to stay ahead of defenses. According to the latest findings from HP Wolf Security, malicious actors are now leveraging a diverse range of malicious documents to spread malware and gain initial access to target systems.
Alex Holland, principal threat researcher at the HP Security Lab, highlighted this shift in focus, noting that threat actors are now prioritizing script-based phishing techniques over traditional malicious documents. This revelation comes ahead of the release of HP Wolf Security’s Threat Insights Report Q2 2024.
Leveraging Archive Files in Phishing Campaigns
Holland explained, “For the past two years, we have seen a movement away from using maldocs towards leveraging interpreted script languages like VBScript and JavaScript.” Threat actors are combining this living-off-the-land phishing technique with the delivery of encrypted archive files.
The report shows that 39.23% of malware deliveries in Q2 2024 came from archive files, which is a significant increase from the previous reporting period.
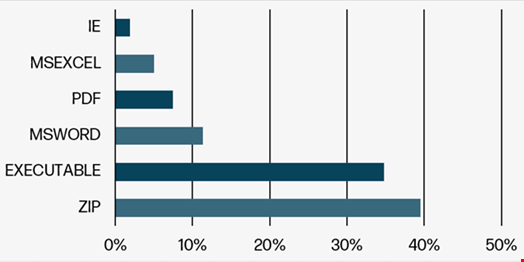
This sophisticated approach is made possible by the use of over 50 different archive file formats, with threat actors exploiting the expanded support for these formats in Windows 11. Organizations are advised to limit unused archive file formats to reduce their attack surface.
Evidence of AI-Generated Malicious Code
The report also highlights other alarming trends in cybercrime, including phishing campaigns using various vectors such as malicious PDF documents and SVG images, malvertising campaigns targeting browsers, and the first evidence of generative AI being used in a malicious campaign.
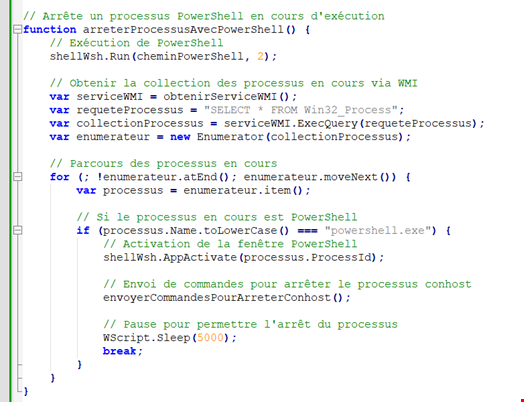
Researchers at the HP Security Lab detected a campaign targeting French speakers that utilized VBScript and JavaScript, believed to have been created with the assistance of GenAI. This AI-generated malware infects users with the AsyncRAT infostealer, showcasing how GenAI is lowering the entry barrier for cybercriminals.


